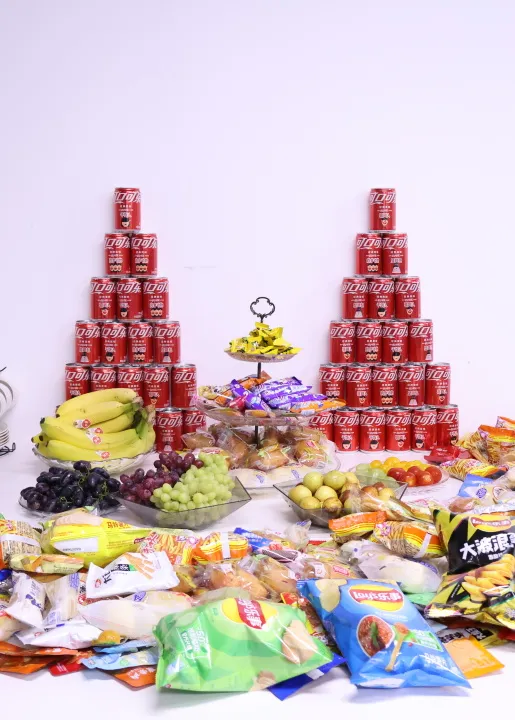
Analysis of Signal Integrity in PCB Design
It is inevitable that ultrahigh speed PCB boardson flex and rigid flex are increasingly used in electronIC products These systems also require ground plane isolation and separation of RF and digital references for wireless protocols High speed and high frequency may cause signal integrity problems, many of which are related to the location and geometry of the middle ground plane A common method of providing a consistent 0 V reference on flexible and rigid flexible boards is to use a hatched line or grid shaped ground plane on the flexible tape This provides a large conductor, which can still provide a mask in a wide frequency range, while still allowing the flexible tape to bend and fold without producing too much rigidity However, signal integrity problems arise in two areas: ensuring consistent track impedance, shielding and isolation, and preventing fiber braid effects in hatch structures
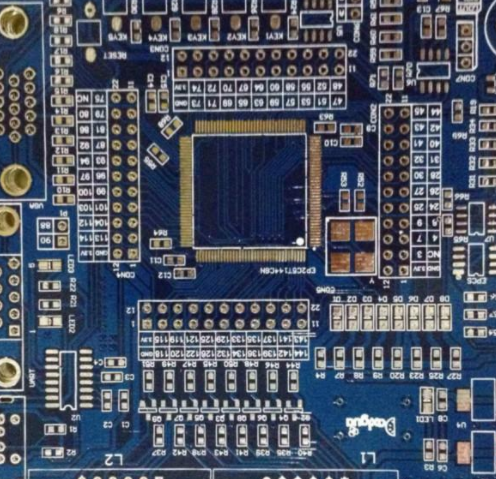
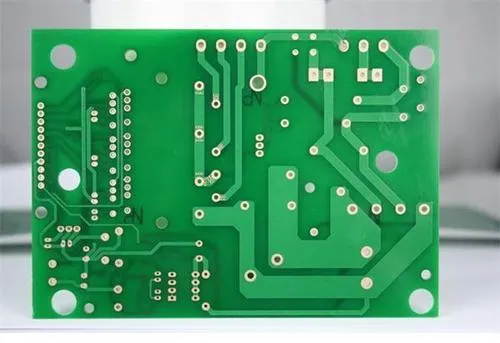
PCB board
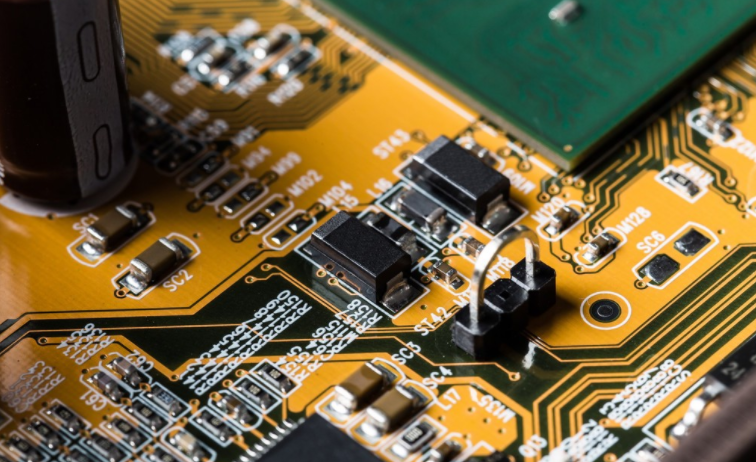
Grid plan design
Basically, hatches work like any other ground plane. It is designed to provide a consistent reference so that the trace can be designed to have the desired impedance. Any common transmission line geometry (microstrip, stripline, or waveguide) can be placed in a rigid flexible or Flexible PCB board with a grid grounding plane. The shadow copper area placed on the surface layer of the flexible band provides almost the same effect as the solid copper at low frequencies. The common configuration of stripline and microstrip wiring on flexible tape with grid grounding plane. This kind of grid can be used on rigid plates, but I have never seen it, nor have customers asked for it. Instead, a grid pattern is used in flexible/rigid flexible plates to balance the impedance control requirements with reasonable flexible tape requirements.
Impedance control
One option for using single ended or differential pairs is to place solid copper in the plane layer directly below the trace and place the grid elsewhere in the circuit. If cabling becoMES very dense, you need to use grids everywhere. If you choose to use meshes, you will have more flexibility, but the mask isolation will be lower, and the impedance control conditions will change. The grid plane structure has two geometric parameters: L and W. These two parameters can be combined as a fill factor or as part of the grid area covered by copper. Changing these parameters will have the following effect: If other parameters remain unchanged, opening the grid area (adding L to add grid openings) will increase the impedance. This also makes the ribbon easier to bend (less force). Adding W while keeping other parameters constant will close the grid area, thus adding impedance. This also makes the ribbon pattern more difficult to bend (using more force). Other parameters that control the impedance of the standard geometry have the same effect when using a grid ground plane. Once you reach the high frequency, you will excite the non electromagnetic mode around the transmission line, and you may even see the effect SIMilar to fiber weaving.
Is there a fiber weaving effect in Flex ribbon?
This is where the grid grounding plane on the PCB is very interesting, because the grid pattern can begin to resemble the glass woven pattern used in FR4 and other laminates. This brings us back to a situation where we must worry about the effect of weaving fibers in the usually smooth and relatively uniform substrate. These effects occur when the bandwidth of the traveling signal overlaps with one or more resonances in the grid. For L=60 mils on the polyimide, the step resonance will be 50 GHz. Whether on rigid PCB or flexible PCB, when digital signal propagates along the track of grid grounding plane, these hatch structures will generate strong radiation. As more Flex applications open at a higher frequency, for some reason, I expect these effects to be worse in Flex ribbon with grid ground plane.
High Q resonance
As in traditional glass woven substrates, the grid forms a cavity structure that supports resonance when excited at a specific frequency. Due to the high conductivity of the cavity wall (copper), these resonators in the grid ground plane will have very high Q values. In this case, there will be lower loss and higher Q resonance. This leads to increased cavity EMIssion and resonant power losses.
Open grid with low isolation
The mesh ground plane generally ensures that any radiated EMI from the fiber optic braided cavity is emitted along the edge of the circuit board Because the mesh has an open cavity, there is less isolation here, and it can also radiate along the surface of the flexible band This has the opposite effect: the trajectory is more radiant, and it is more susceptible to external EMI To solve these problems, use a tighter grid, just as use a tighter glass braid to prevent fiber braiding effects Flexible and rigid flexible PCBs will continue to become PCB space and become more advanced through updated manufacturing capabilities
然后
聯系
電話熱線
13410863085Q Q
微信

- 郵箱